Zhouyi (called 周易) classics is an ancient Chinese book for studying and measuring the rotation, transformation and unchanging laws of all things in the universe,including the Yijing (called 易经)and Yilegend (called 易传) 。The “ZhouYi” listed on this website refers to the “Commentary on the Thirteen Classics – ZhouYi Justice” (《十三经注疏-周易正义》) published by Peking University Press in China in 1999,compiled by the Commentary Committee of the Thirteen Classics,and edited by Li Xueqin (李学勤,1933-2019)。 I would like to express my special thanks to the editors and publishers of the book。This website refers to the Chinese ideological and cultural terminology that has been published in the “Chinese Thought and Culture Terminology Dissemination Project (中华思想文化术语传播工程)” implemented by the Foreign Language Teaching and Research Press of Beijing University of Foreign Chinese,and some of the terms have been modified to facilitate prediction activities。
Three characteristics of Zhouyi
- The term “rotation” pertains to the cyclic occurrences of sunrise and moonset, or the seasonal shift from winter to spring marked by tree sprouting, flower blooms and falling leaves。
- The concept of “transformation” in Zhouyi emphasizes the interworking and interconnection between heaven and earth through Cathode-gas( called 阴气 )and Anode-air(called 阳气 )——Or rather,the Qi (气) of Yin (阴) and Yang (阳) 。This analogy, similar to the cathode and anode of a battery, highlights their invisible, inaudible nature and elusive target。The ancients held the belief that the universe, as well as human beings, were formed by the interaction of Cathode-gas and Anode-air。
- The term “unchanging” signifies the immutability of the celestial and terrestrial positions, with heaven being elevated above and earth assuming its ordinary position below。Each entity occupies its designated place without any disturbances or disruptions。
There are three versions of Zhouyi
Lianshan(called 连山) by Shennong (called 神农) in ancient times, Guizang (called 归藏) by Huangdi(called 黄帝), and Zhouyi by King Zhouwen(called 周文王)。
Fuxi Taiji and Eight Gua Diagrams
As shown above,Taiji grows Two Yi(called 两仪)or Two Modes,include Anode-air(abbreviated as the character A) and Cathode-gas(abbreviated as the character C),two Yi superposition Four symbol (called 四象)or Four Images。
Like theories of the Big Bang or the central singularity of black holes ,Fuxi (伏羲) believed that the starting point of the universe was Taiji (太极), Fuxi employed a lengthy line to symbolize the concept of Anode-air,suchas “——” ;while utilizing two shorter lines to represent Cathode-gas,such as “— —”。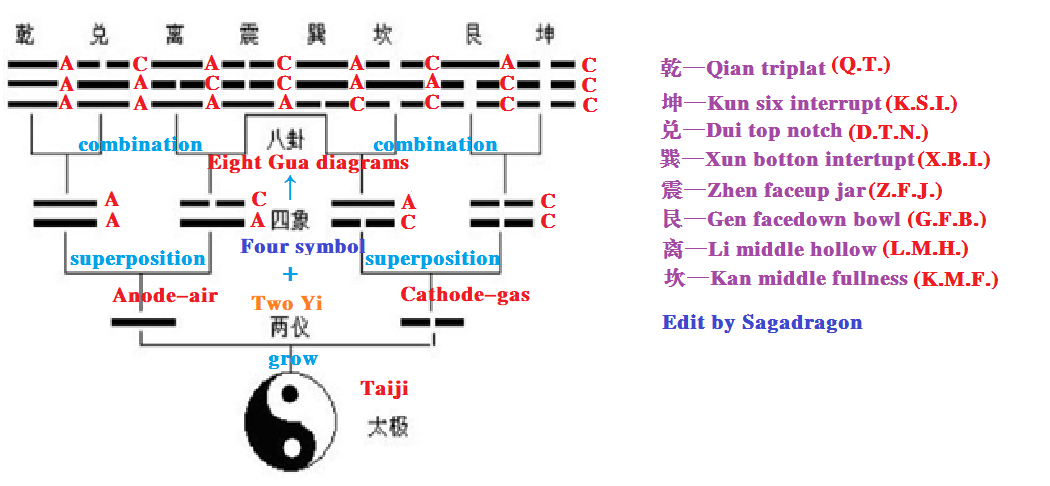
- If you superimpose Anode-air on top of Anode-air,such as A on top of A, it makes Old-Anode(called 老阳);
- If you superimpose Cathode-gas on top of Anode-air,such as C on top of A, it makes Young-Cathode(called 少阴,read from the top down as CA);
- If you superimpose Cathode-gas on top of Cathode-gas, such as C on top of C,it makes Old-Cathode(called 老阴);
- If you superimpose Anode-air on top of Cathode-gas, such as A on top of C, it makes Young-Anode(called 少阳, read from the top down as AC)。
Two Yi superimpose on top of Four symbol makes Eight Gua diagrams(called 八卦) or Eight Trigrams,abbreviate to E.G.D.。The top of picture above goes from left to right:
- Anode-air superimpose on top of Old-Anode ,such as A superimpose on top of AA,makes Qian Triplat(calles 乾卦),abbreviate to Q.T.
 ;
;
- Cathode-gas superimpose on top of Old-Anode ,such as C superimpose on top of AA,makes Dui Top Notch(calles 兑卦),abbreviate to D.T.N.
 ;
;
- Anode-air superimpose on top of Young-Cathode, such as A superimpose on top of CA,makes Li Middle Hollow(called 离卦),abbreviate to L.M.H.
 ;
;
- Cathode-gas superimpose on top of Young-Cathode ,such as C superimpose on top of CA,makes Zhen Faceup Jar(called 震卦),abbreviate to Z.F.J.
 ;
;
- Anode-air superimpose on top of Young-Anode ,such as A superimpose on top of AC,makes Xun Botton Interrupt(calles 巽卦),abbreviate to X.B.I.
 ;
;
- Cathode-gas superimpose on top of Young-Anode ,such as C superimpose on top of AC,makes Kan Middle Fullness(calles 坎卦),abbreviate to K.M.F.
 ;
;
- Anode-air superimpose on top of Old-Cathode,such as A superimpose on top of CC,makes Gen Facedown Bowl(called 艮卦) ,abbreviate to G.F.B.
 ;
;
- Cathode-gas superimpose on top of Old-Cathode,such as C superimpose on top of CC,makes Kun Six Interrupt(called 坤卦) ,abbreviate to K.S.I.
 。
。
The structure of Yijing
Eight Gua Diagrams superimpose each other makes Sixty-four Gua Designs (called 64卦象),contain Gua dictionary (called 卦辞) and senary-diction (called 爻辞) ,or Hexagram Texts (卦爻辞)。Each Gua Designs consisting of six lines, then sixty-four Gua designsresulting in a total of 384 lines。Two Eight Gua Diagrams had called by a joint name for the upper and lower,such as “Q.T. upper and Q.T. lower”,Q.T. superimpose on top of itself makes Qian-is-heaven (called 乾为天),abbreviate to Q.I.H.。K.S.I. superimpose on top of itself makes Kun-is-earth (called 坤为地),abbreviate to K.I.E.。Q.I.H. has an extra “Use nine” senary-diction (called 用九),and K.I.E. has an extra “Use six” senary-diction (called 用六)。Because of the addition “Use nine” and “Use six”,final Yijing has 386 lines ,corresponding has 386 senary-diction。The Yijing writted style is both ancient and profound。

Include Q.I.H. and K.I.E.,other sixty-two Gua Designs combinations respectively as follows:
- Q.T. upper and X.B.I. lower called Wive Gua,姤卦 in Chinese;
- Q.T. upper and G.F.B. lower called Hide Gua,遯卦 in Chinese;
- Q.T. upper and K.S.I. lower called Bad Gua ,否卦 in Chinese;
- X.B.I. upper and K.S.I. lower called Observe Gua,观卦 in Chinese;
- G.F.B. upper and K.S.I. lower called Spalling Gua,剥卦 in Chinese;
- L.M.H. upper and K.S.I. lower called Promotion Gua,晋卦 in Chinese;
- L.M.H. upper and Q.T. lower called Magnanimous Gua,大有卦 in Chinese;
- K.S.I. upper and Z.F.J. lower called Return Gua,复卦 in Chinese;
- K.S.I. upper and D.T.N. lower called Go To Place Gua,临卦 in Chinese;
- K.S.I. upper and Q.T. lower called Calm Gua,泰卦 in Chinese;
- Z.F.J. upper and Q.T. lower called Grand Gua,大壮卦 in Chinese;
- D.T.N. upper and Q.T. lower called Decision Gua,夬卦 in Chinese;
- K.M.F. upper and Q.T. lower called Wait Gua,需卦 in Chinese;
- K.M.F. upper and K.S.I. lower called Circle of Friends Gua,比卦 in Chinese;
- D.T.N. upper and D.T.N. lower called Talk Gua,泽卦 in Chinese;
- D.T.N. upper and K.M.F. lower called Trapped Gua,困卦 in Chinese;
- D.T.N. upper and K.S.I. lower called Collect Gua,萃卦 in Chinese;
- D.T.N. upper and G.F.B. lower called Marry Gua,咸卦 in Chinese;
- K.M.F. upper and G.F.B. lower called Take Refuge Gua,蹇卦 in Chinese;
- K.S.I. upper and G.F.B. lower called Modesty Gua,谦卦 in Chinese;
- Z.F.J. upper and G.F.B. lower called Slight Error Gua,小过卦 in Chinese;
- Z.F.J. upper and D.T.N. lower called Lover Gua,归妹卦 in Chinese;
- L.M.H. upper and L.M.H. lower called Fire Gua,火卦 in Chinese;
- L.M.H. upper and G.F.B. lower called Travel Gua,旅卦 in Chinese;
- L.M.H. upper and X.B.I. lower called Innovation Gua,鼎卦 in Chinese;
- L.M.H. upper and K.M.F. lower called Failed Gua,未济卦 in Chinese;
- G.F.B. upper and K.M.F. lower called Ignorance Gua,蒙卦 in Chinese;
- X.B.I. upper and K.M.F. lower called Escape Gua,涣卦 in Chinese;
- Q.T. upper and K.M.F. lower called Lawsuit Gua,讼卦 in Chinese;
- Q.T. upper and L.M.H. lower called Concentric Gua,同人卦 in Chinese;
- Z.F.J. upper and Z.F.J. lower called Thunder Gua,雷卦 in Chinese;
- Z.F.J. upper and K.S.I. lower called Drum Gua,豫卦 in Chinese;
- Z.F.J. upper and K.M.F. lower called Rescue Gua,解卦 in Chinese;
- Z.F.J. upper and X.B.I. lower called Constant Gua,恒卦 in Chinese;
- K.S.I. upper and X.B.I. lower called Rise Gua,升卦 in Chinese;
- K.M.F. upper and X.B.I. lower called Well Gua,井卦 in Chinese;
- D.T.N. upper and X.B.I. lower called Gross Negligence Gua,大过卦 in Chinese;
- D.T.N. upper and Z.F.J. lower called Opportune Gua,随卦 in Chinese;
- X.B.I. upper and X.B.I. lower called Wind Gua,风卦 in Chinese;
- X.B.I. upper and Q.T. lower called Weak Animal Gua,小畜卦 in Chinese;
- X.B.I. upper and L.M.H. lower called Family Member Gua,家人卦 in Chinese;
- X.B.I. upper and Z.F.J. lower called Beneficial Gua,益卦 in Chinese;
- Q.T. upper and Z.F.J. lower called Awedly Gua,无妄卦 in Chinese;
- L.M.H. upper and Z.F.J. lower called Punishment Gua,噬嗑卦 in Chinese;
- G.F.B. upper and Z.F.J. lower called Cheek Gua,颐卦 in Chinese;
- G.F.B. upper and X.B.I. lower called Venomous Insect Gua,蛊卦 in Chinese;
- K.M.F. upper and K.M.F. lower called Water Gua,水卦 in Chinese;
- K.M.F. upper and D.T.N. lower called Rule Gua,节卦 in Chinese;
- K.M.F. upper and Z.F.J. lower called Thunderstorm Gua,屯卦 in Chinese;
- K.M.F. upper and L.M.H. lower called Succeed Gua,既济卦 in Chinese;
- D.T.N. upper and L.M.H. lower called Revolution Gua,革卦 in Chinese;
- Z.F.J. upper and L.M.H. lower called Abundant Gua,丰卦 in Chinese;
- K.S.I. upper and L.M.H. lower called Expedient Gua,明夷卦 in Chinese;
- K.S.I. upper and K.M.F. lower called Majority Gua,师卦 in Chinese;
- G.F.B. upper and G.F.B. lower called Mountain Gua,山卦 in Chinese;
- G.F.B. upper and L.M.H. lower called Civilization Gua,贲卦 in Chinese;
- G.F.B. upper and Q.T. lower called Strong Animal Gua,大畜卦 in Chinese;
- G.F.B. upper and D.T.N. lower called Loss Gua,损卦 in Chinese;
- L.M.H. upper and D.T.N. lower called Dissent Gua,睽卦 in Chinese;
- Q.T. upper and D.T.N. lower called Fulfil Gua,履卦 in Chinese;
- X.B.I. upper and D.T.N. lower called Equally Integrity Gua,中孚卦 in Chinese;
- X.B.I. upper and G.F.B. lower called Gradually Gua,渐卦 in Chinese。
The difference between Eight Gua Diagrams and Sixty-four Gua Designs
When we say the Qian triplat ,refer to Eight Gua Diagrams, and Qian-is-heaven refer to Sixty-four Gua Designs,these two formulations will appear in different situations in the forecast,other Eight Gua Diagrams is the same thing。The Sixty-four Gua Designs usually appears in the Senary-Layer-Divination Gua (called 六爻卦) ,or Plum blossom Gua Count (called 梅花易数)。The Eight Gua Diagrams comes up in almost every divination,except for the Polaris With Big Dipper Count (called 紫微斗数)。
The structure of Yi Legend《易传》
Yi Legend serves as an elucidation of the Yijing,encompassing ten chapters:
- The Tuan, known as “彖”,is divided into two chapters consisting of 64 articles。 It provides explanations on the names of Sixty-four Gua Designs,a Gua dictionary,and an outline。
- The Design,referred to as “象”,is also divided into two chapters with 64 articles。 It offers explanations on the design of Sixty-four Gua and senary-diction。
- Classical Chinese, known as “文言”,serves as a supplementary exposition of the Q.I.H and K.I.E.,believed to be written by Confucius(孔子551 BC – 479 BC)。
- The Attach Dictionary,called “系辞”, provides a general overview and discussion of the Yijing.。One section expresses the subtle principles of Yijing while the other showcases important examples of reading Yijing。It is also divided into two chapters。
- The Narrate Gua,called”说卦” explains the origin of the Yijing and delves into the meaning behind each Eight Gua Diagrams。
- The Sequence of Gua,called”序卦” is an outline that arranges Sixty-four Gua Designs in Zhouyi,revealing their interrelation between designs。
- The Different versions Gua,called”杂卦” uses different names for Sixty-four Gua Designs symbolizing various aspects in our world.
The Western Han Dynasty in China witnessed the extensive study and active promotion of Zhouyi by Jiao Yanshou (焦延寿) and Jing -fang (京房,77BC – 37BC)——The two of them have a master-apprentice relationship。Their notable contributions involved incorporating the Trunk Of Sky (天干,similar to the torso of the sky,used to record every day) and the Branch Of Earth (地支,it divides the whole earth into twelve branches,can also used to record every day) into the Eight Gua Diagrams, which ultimately formed the foundation of today’s gossip。The year,month,day,and hour of each person’s birth can be represented by the two characters of the Trunk Of Sky and the Branch Of Earth,so it is called the Fate Of Eight Characters(八字)。
The Plum Blossom Heart Of Yi (梅花心易), authored by Shao Yong (邵雍,January 21, 1012 – July 27, 1077) during the ancient Song Dynasty in China, represents another significant branch of study,and it is also the development of Plum blossom Gua Count。
The combination of Zhouyi with RiverMap (called 河图) and LuoBook (called 洛书) produced a more advanced forecasting technique,such as Miraculous Eight Way Hide Jia (called 八门遁甲,or 奇门遁甲),and Great Six Responsible (called 大六壬)。Fan Li (范蠡,536 BC – 448 BC) in the late Spring and Autumn Period of ancient China was an outstanding representative of the Great Six Responsible。While Jiang Ziya (姜子牙,1128 BC – 1016 BC) and Zhang Zifang (张子房, ? -186 BC) as the representative of the strategist and strategist improved the Miraculous Eight Way Hide Jia, which became the highest achievement of ZhouYi。These prediction theory has been tested for thousands of years and is still accurate。